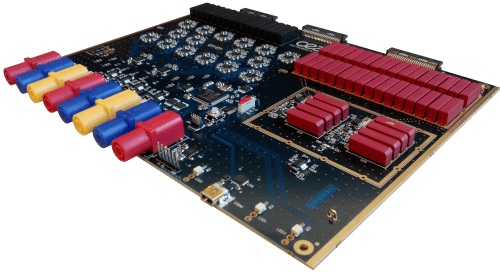
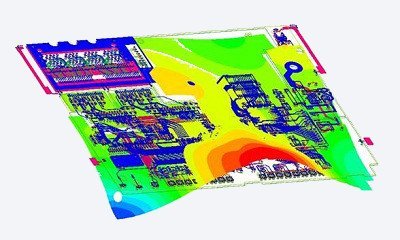
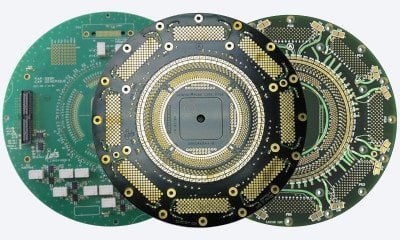
Product Industrialisation
From Design to Production
To guarantee the reliability and the quality of the electronic products that we realize, we have a department dedicated to industrialisation. It defines, in close collaboration with the designers and the customer, all the methods and tools to design an industrialized product (reliable and adapted to production technologies). With this service, we can meet the most stringent functional, normative and qualitative requirements.
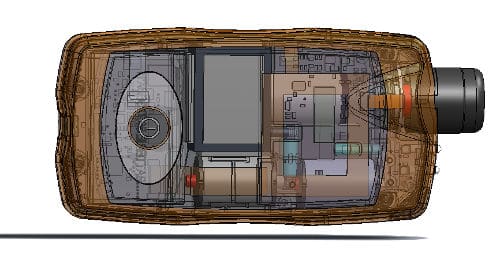
Design For X
We apply the DFX approach (Design For eXcellence) which covers all the rules to be observed during the study to improve the product design according to the priority requirements of the specifications.
Cost (DFC)
Priority to global solutions reducing the final cost of the product, both in terms of components achitecture and process.
Constraint (DFCO)
Reliability optimized by performing the mission profile and the qualification plan including: Preliminary environmental tests, highly accelerated life tests (HALT), failure mode analysis, EMC testing, MTBF calculation…
Manufacturing (DFM)
Definition of the technologies and the partners (EMS) able to implement them. The more you comply with the rules of DFM, the more you get high returns easily and an optimized MTBF.
Test (DFT)
FMEA approach for components, testability analysis, optimization of test coverage and planing of the means to be implemented.
Assembly (DFA)
Easy assembly and disassembly of the product, without risk of breakage and loss of time.
Supply Chain (DFS)
Analysis of the know-how necessary for the manufacturing process, concentration of tasks, removal of unnecessary transfers.
Maintenance (DFMa)
Analysis and definition of diagnostic tools and quick troubleshooting. Optimizes the availability rate of products in their life cycle.
Environment (DFE)
Energy optimization, dismantling analysis, optimization of the product recyclability rate …
Achievements

Electronic box
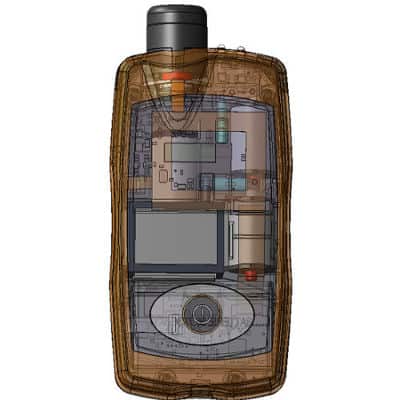

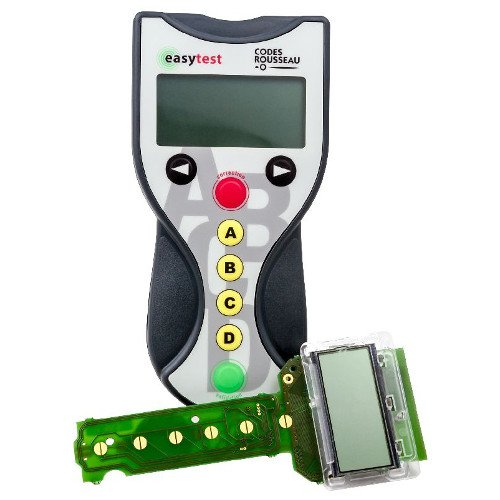
Sampling device
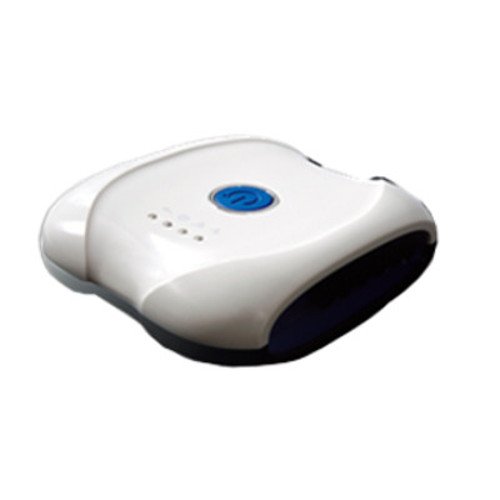

Medical device
Methodology
The process of industrialisation improves the product in a global approach “DFX” which involves the design office and the factory as soon as the needs are defined: On the factory side, the industrialisation engineer (product study) and the methods engineer (factory) must work together on the manufacturing constraints especially on the cost, time to market, efficiency and reliability aspects. On the design side, the industrialisation engineer works with the product designer and the other DFX partners to identify and apply the best solutions to meet the challenges of the specifications and the next production. The methods will easily adapt the tools of the factory to manufacture the industrialized product.
Feasibility
- Technical and economic feasibility study of the project (state of the art, risk analysis …),
- Specifications to define technical and functional specifications,
- Selection and qualification of service providers / partners for each skill requirement (mechanics, plastics, assembly, testing, etc.).
Design
- Addition of design guidelines according to each “X” constraint of the DFX approach: IPC rules, norms, cost, testability, reliability, maintainability, etc …,
- Validation of technologies and techniques selected for the realization of the product (components, assembly …),
- Realization of a model to simulate a part of the electronic, mechanical and software applciations,
- Technical evaluation from the model (measurements, functions, tests, EMC …).
Production
- Selection of suppliers and management of components (supply, storage, obsolescence …),
- Realization of hardware and software testing tools to ensure the best test coverage,
- Realization of industrial prototypes integrating the electronic, software and mechanical functions of the final product, with production tools,
- CE marking in relation with the notified bodies for carrying out conformity tests,
- Realization of a representative pre-series to prepare the mass production of the product.
Quality
- Quality management system according to the requirements of ISO 9001,
- Implementation of tools for quality management (SCP, FMEA ..),
- Continuous process improvement to reduce delays and reduce costs,
- Definition and organization of preventive and corrective maintenance.
Other services of our design office
Electronic design
Design services for electronic cards and embedded systems, from feasibility study to manufacturing …
Embedded software
Low level embedded software development for embedded systems based on 8, 16 or 32 bit microcontrollers. With expertise in …
Simulation
Electronic circuit simulation service: simulation and measurement of the parameters of a microstrip line, HF (Up to 70Ghz), signal integrity …
Test boards
Test card design and manufacturing service for semiconductor components with socket or custom test tools…
Need a pre-study or an estimate ?
Please complete the form below.